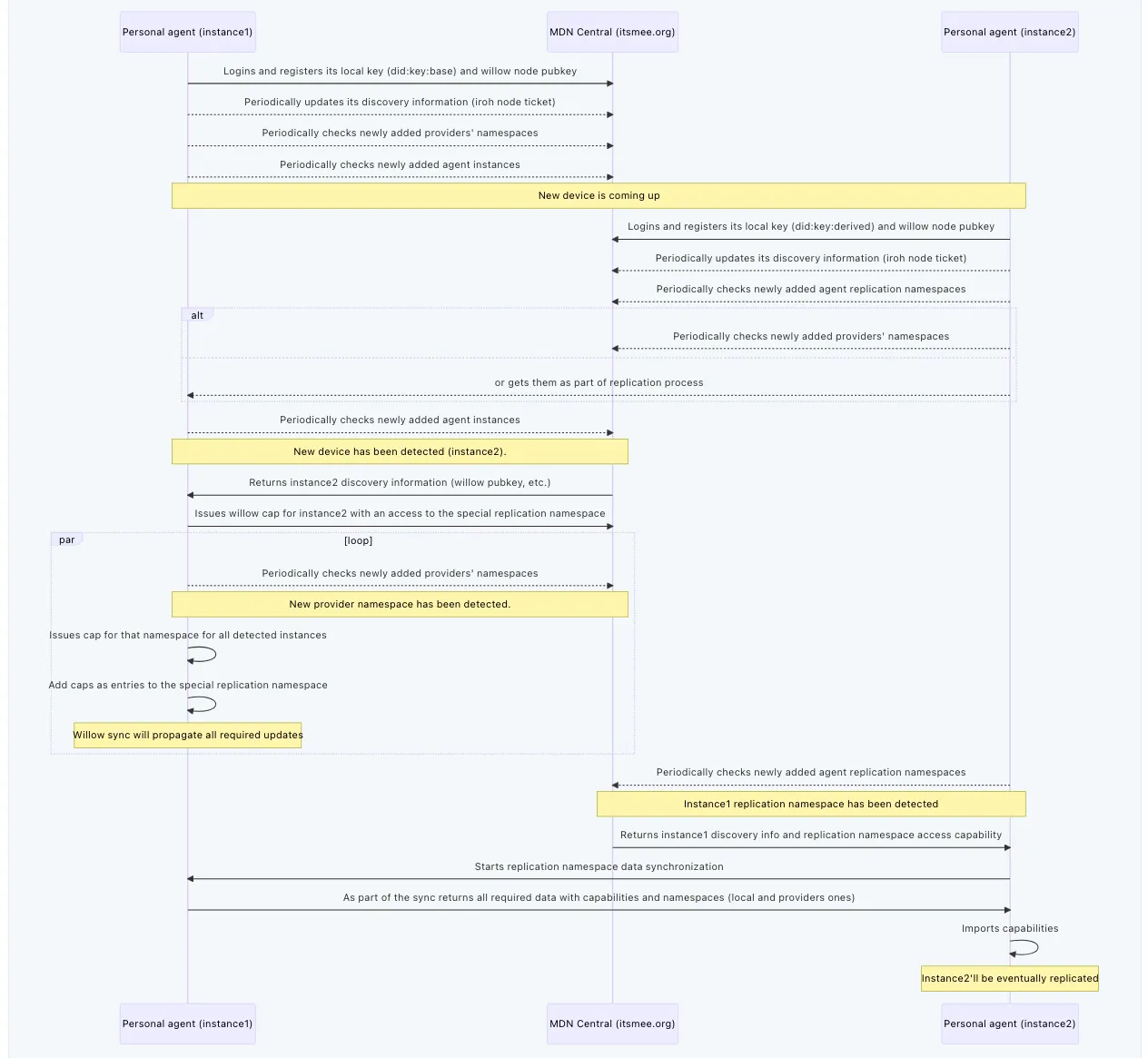
Data synchronization
The Mee Data Network implements data synchronization between nodes through a layered architecture using the Willow protocol for data sync logic and iroh for peer-to-peer networking.
Architecture Overview
Protocol Stack
- MDN Layer: User control of data flows across the network
- Willow Layer: Low-level delegation and data synchronization
- iroh Layer: P2P data connections
Network Communication
The iroh libraries
The network layer uses two main libraries from the iroh project:
iroh-net
- Establishes direct connectivity between peers
- Uses QUIC protocol for connections
- Identifies connections using ed25519 keypairs
- Handles NAT traversal
- Manages fallback to relay servers when needed
iroh-bytes
- Manages data streaming between peers
- Built on top of QUIC protocol
- Works with content-addressed data blobs
- Verifies data integrity of each stream chunk using BLAKE3
Establishing a connection
The system prioritizes direct peer-to-peer connections between nodes using iroh’s QUIC-based networking stack.
When direct P2P connections aren’t possible, the system falls back to using relay servers. These relays temporarily route encrypted traffic until a direct connection can be established, but step back if a direct path becomes available.
For specific details about connection establishment and fallback conditions, see the iroh documentation.
Synchronization Process
Initial Device Setup
When a device joins the network:
- MDN Central facilitates initial peer discovery
- The device establishes connections with relevant peers
- Synchronization begins based on capability tokens and sharing permissions
Ongoing Sync
- Synchronization happens automatically between authorized nodes
- Uses Willow’s partial sync capabilities to synchronize only relevant data subsets
- Private area intersection allows peers to determine shared data without leaking information
- All synchronization respects capability-based access controls
Conflict Resolution
The sync system uses Willow’s conflict resolution mechanism. Willow uses state-based CRDTs, which ensure eventually consistent states across nodes.
For details about partial sync constraints, private area intersection mechanics or the conflict resolution mechanism, see the Willow specification.
Here’s a detailed overview of the synchronization process